Activated Carbon Filter
I. Product Overview
Activated carbon is currently the most widely used adsorbent. It is produced from raw materials such as coal, charcoal, fruit pits, and fruit shells through high-temperature carbonization and activation processes. This results in a unique porous structure with various shapes of micro-pores in its crystalline lattice, providing a large specific surface area (ranging from 800 to 2000 square meters per gram of activated carbon). Consequently, it exhibits exceptional adsorption capacity. Activated carbon filters can effectively remove organics, colloids, heavy metals, residual chlorine, and other unpleasant odors from water, reducing water color. They are widely used in water purification for factories and towns, as well as in pretreatment processes for reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and ion exchange systems, to enhance the inlet water quality of various advanced purification equipment.
II. Operating Principle
The adsorption principle of activated carbon involves forming a balanced surface concentration on its particle surface. The size of activated carbon particles also affects its adsorption capacity. Generally, smaller activated carbon particles result in a larger filtration area. Therefore, powdered activated carbon has the largest total surface area and the best adsorption effect, but it is prone to flowing into the water tank and is difficult to control, making it rarely used. Granular activated carbon, due to its particle shape and stability, is not prone to flowing and blocking within the filter layer. It exhibits strong adsorption capacity and is convenient to carry and replace. The adsorption capacity of activated carbon is directly proportional to the contact time with water; the longer the contact time, the better the filtered water quality. Note: The filtered water should flow out of the filter layer slowly. New activated carbon should be washed cleanly before first use to avoid dark-colored water discharge. Before installing activated carbon in the filter, 2 to 3 centimeters of sponge should be placed at the bottom and top to prevent algae and other large particle impurities from penetrating. After 2 to 3 months of use, if the filtration effect decreases, the activated carbon should be replaced, and the sponge layer should also be replaced regularly. The pressure vessel of the activated carbon filter is filled with a coarse quartz sand cushion layer and high-quality activated carbon. A balanced surface concentration forms on the surface of the activated carbon particles, which then adsorbs organic impurities into the particles. The adsorption effect is high during initial use. However, over time, the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon will weaken to varying degrees, and the adsorption effect will also decrease. If the water quality in the aquarium is turbid and contains high levels of organics, the activated carbon will quickly lose its filtering function. Therefore, activated carbon should be cleaned or replaced regularly.
Adsorption Principle:
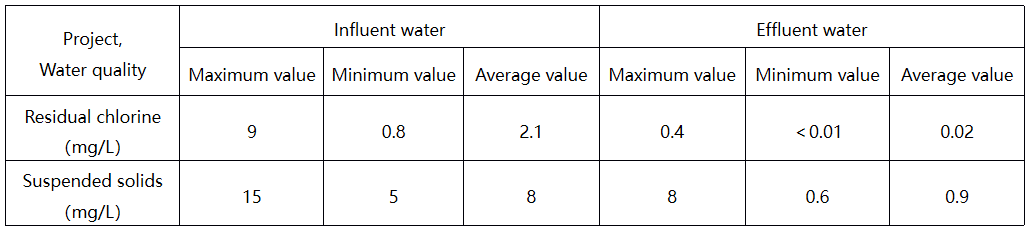
This equipment can remove discoloration, odors, and heavy metals such as mercury, lead, cadmium, zinc, iron, manganese, and chromium from clear water. It can also remove arsenic, hydrides, sulfides, residual chlorine, and other polymeric compounds, as well as radioactive substances such as strontium and radium. It removes and kills bacteria, Escherichia coli, and other carcinogens in water. It is an ideal water supply equipment for purifying water in industries such as drinking water, food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. The activated carbon filter has a simple structure and is convenient for operation and maintenance.
III. Technical Characteristics
1.High Efficiency: It can operate continuously for 24 hours without the need for shutdown backwashing.
2.Low Operating Costs: It does not require a high-lift, high-flow backwash pump.
3.Low Maintenance Costs: During operation, apart from the quartz sand filter media, there are no rotating parts, resulting in low failure rates and maintenance costs.
4.Low Initial Investment: It does not require separate coagulation tanks, clarification tanks, or other facilities. It also does not require backwash pumps, electric or pneumatic valves, etc., reducing engineering workload and initial investment.
5.Low Head Loss: With a single filter media and timely cleaning, head loss is minimized, with a total head loss ≤0.5m.
6.Flexible Inlet Water Quality Requirements: It can tolerate inlet water quality with an SS concentration of 150mg/L for long periods and short-term impacts of up to 300mg/L SS without compromising outlet water quality.
7.Stable Outlet Water Quality and Excellent Filtration Effect: Timely cleaning of the filter media ensures high-quality, stable outlet water with no periodic fluctuations in water quality.
8.Compact Size and Aesthetic Appearance: By integrating the traditional three-stage wastewater treatment process, it saves about 70-80% of land use and has a more aesthetic and compact appearance.

.jpg)
.jpg)


